Introduction:
Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal computer (PC) market with over 90% market share, overtaking Mac OS, which had been introduced in 1984. Apple came to see Windows as an unfair encroachment on their innovation in GUI development as implemented on products such as the Lisa and Macintosh (eventually settled in court in Microsoft's favor in 1993). On PCs, Windows is still the most popular operating system. However, in 2014, Microsoft admitted losing the majority of the overall operating system market to Android, because of the massive growth in sales of Android smartphones. In 2014, the number of Windows devices sold was less than 25% that of Android devices sold. This comparison however may not be fully relevant, as the two operating systems traditionally target different platforms. Still, numbers for server use of Windows (that are comparable to competitors) show one third market share, similar to for end user use.
As of December 2017, the most recent version of Windows for PCs, tablets, smartphones and embedded devices is Windows 10. The most recent versions for server computers is Windows Server 2016. A specialized version of Windows runs on the Xbox One video game console.
1- Windows Interface Manager
The history of Windows dates back to 1981, when Microsoft started work on a program called "Interface Manager". It was announced in November 1983 (after the Apple Lisa, but before the Macintosh) under the name "Windows", but Windows 1.0 was not released until November 1985.
 |
| The ever-present boot screen. Please note that the 'Internal Test Release' number means absolutely nothing. It's just to make it look good. |
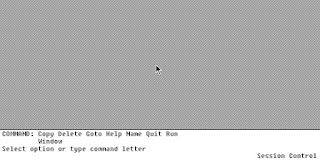 |
| The 'Session Control' menu. This looks like a very early precursor to the 'Start' menu and icon tray in Windows 9x and above. |
 |
| BASIC86 running in a window. |
 |
| Word for DOS running in a window. |
 |
| The first 'DOS Box,' you might say! An MS-DOS 2.00 Command Prompt, running in a window. |
 |
| Word for DOS and Multiplan running in tiled windows. |
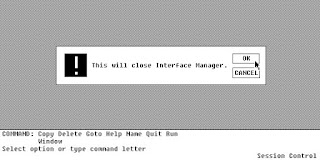 |
| Shutting down Interface Manager. Similar to Windows 1.x, 2.x, 3.x, and Windows NT 3.x. |
2- Windows 1.0

Windows 1.0 is a graphical personal computer operating environment developed by Microsoft. Microsoft had worked with Apple Computer to develop applications for Apple's January 1984 original Macintosh, the first mass-produced personal computer with a graphical user interface (GUI) that enabled users to see user friendly icons on screen. Windows 1.0 was released on November 20, 1985, as the first version of the Microsoft Windows line. It runs as a graphical, 16-bit multi-tasking shell on top of an existing MS-DOS installation. It provides an environment which can run graphical programs designed for Windows, as well as existing MS-DOS software. Its development was spearheaded by the company founder Bill Gates after he saw a demonstration of a similar software suite known as Visi On at COMDEX.
Windows 1.0 could only support tiled windows, but had desktop features such as the MS-DOS Executive file manager, Calendar, Cardfile, Notepad, Terminal, Calculator and Clock.
Utilities included RAMDrive, for managing memory cards designed to beat the PC's 640KB memory limit, Clipboard and Print Spooler. There was even a game, Reversi. In a special introductory offer, Windows 1.0 came with Windows Write and Windows Paint and cost $99.
3- Windows 2.0
The second version of Windows introduced overlapping windows and supported 16-colour VGA graphics. It marked the debut of the Control Panel and Program Information Files, or PIFs, that told Windows how to run DOS applications,. It was also the first Windows platform for Microsoft's Word and Excel applications.
Like Windows 1.0, version 2.0 could run on a dual-floppy-drive PC without a hard disk. It used the real-mode memory model, limiting memory access to 1MB.
Overlapping windows and other Mac-like features in Windows 2.0 resulted in an ultimately unsuccessful Apple lawsuit in 1988.
4- Windows 3.0
Windows 3.0, a graphical environment, is the third major release of Microsoft Windows, and was released on May 22, 1990. It became the first widely successful version of Windows and a rival to Apple Macintosh and the Commodore Amiga on the graphical user interface (GUI) front. It was followed by Windows 3.1.
The first Windows version to achieve widespread use, Windows 3.0 saw significant user interface changes, as well as improved exploitation of the Intel 286 and 386 processors' memory management capabilities.
Program Manager and File Manager made their first appearance here, along with a redesigned Control Panel and Solitaire -- a Windows staple to this day. Everything looked better thanks to Windows 3.0's support for 256-colour VGA.
5- Windows 3.1
Windows 3.1x (codenamed Janus) is a series of 16-bit operating environments produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers. The series began with Windows 3.1, which was first sold during April 1992 as a successor to Windows 3.0. Subsequent versions were released between 1992 and 1994 until the series was superseded by Windows 95. During its lifespan, Windows 3.1 introduced several enhancements to the still MS-DOS-based platform, including improved system stability, expanded support for multimedia, TrueType fonts, and workgroup networking.
Windows 3.1 was originally released on April 6, 1992; official support for Windows 3.1 ended on December 31, 2001, and OEM licensing for Windows for Workgroups 3.11 on embedded systems continued to be available until November 1, 2008.
6- Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1 is a 32-bit operating system developed by Microsoft, and released on July 27, 1993. It was the first published edition of the Windows NT series of operating systems.
Windows NT was born from the wreckage of Microsoft's ill-fated OS/2 partnership with IBM. It was built from the ground up under the leadership of ex-DEC software engineer Dave Cutler as a fully 32-bit pre-emptive multitasking, multithreaded, multiprocessing, multiuser operating system with a hybrid kernel and a hardware abstraction layer to facilitate porting between processor platforms.
It was initially developed for the Intel i860, whose N-Ten codename gave NT its name, although later marketing-led revisionism changed this to New Technology. NT variants have appeared on many CPU architectures, including IA-32, x86-64, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC, ARM and Itanium. Its code base still underpins the current generation of Windows operating systems.
7- Windows NT 3.51
Windows NT 3.51 is the third release of Microsoft's Windows NT line of operating systems. It was released on 30 May 1995, nine months after Windows NT 3.5, and three months before the release of Windows 95. The release provided two notable feature improvements; firstly NT 3.51 was the first of a short-lived outing of Microsoft Windows on the PowerPC architecture. The second most significant enhancement offered through the release was that it provides client/server support for interoperating with Windows 95, which was released three months after NT 3.51. Windows NT 4.0 became its successor a year later; Microsoft continued to support Windows NT 3.51 until 31 December 2001.
New features introduced in Windows NT 3.51 include PCMCIA support, NTFS file compression, replaceable WinLogon (GINA), 3D support in OpenGL, persistent IP routes when using TCP/IP, automatic display of textual descriptions when the mouse pointer was placed on toolbar buttons ("tooltips") and support for Windows 95 common controls.
In view of the significant difference in the kernel base, Windows NT 3.51 is readily able to run a large number of Win32 applications designed for Windows 95.
8- Windows 95
Windows 95 (codenamed Chicago) is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged Microsoft's formerly separate MS-DOS and Windows products. It featured significant improvements over its predecessor, Windows 3.1, most notably in the graphical user interface (GUI) and in its simplified "plug-and-play" features. There were also major changes made to the core components of the operating system, such as moving from a mainly co-operatively multitasked 16-bit architecture to a 32-bit preemptive multitasking architecture.
Windows 95's UI saw the first appearance of the long-running features such as the Start button and menu - hence Start Me Up - the taskbar and system tray or notification area, and maximise, minimise, close buttons on windows. The start-up jingle for Windows 95 was written by Brian Eno, ironically, on a Mac.
9- Windows NT 4.0
Windows NT 4.0 is a preemptively multitasked graphical operating system, designed to work with either uniprocessor or symmetric multi-processor computers. It was part of Microsoft's Windows NT family of operating systems and was released to manufacturing on 31 July 1996. It is a 32-bit operating system available in both workstation and server editions with a graphical environment similar to that of Windows 95.
Under the surface, NT 4.0 saw a number of architectural improvements. In particular, the Graphics Device Interface, or GDI, was moved into kernel mode, giving a significant performance boost over NT 3.5x, although this also required graphics and printer drivers to be updated. NT 4.0 was also the first Windows version to support the DirectX multimedia API.
10- Windows 98
Windows 98 (codenamed Memphis while in development) is a graphical operating system by Microsoft. It is the second major release in the Windows 9x line of operating systems and the successor to Windows 95. It was released to manufacturing on May 15, 1998 and to retail on June 25, 1998.
Windows 98 was even more consumer-friendly than its predecessor Windows 95. A range of user-interface enhancements were introduced via the bundled Internet Explorer 4's Windows Desktop Update, including the Quick Launch toolbar, Active Desktop, the ability to minimise a window by clicking its toolbar icon, plus backward and forward buttons, and an address bar, in Windows Explorer.
11- Windows 2000
Windows 2000 is an operating system for use on both client and server computers. It was produced by Microsoft and released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and launched to retail on February 17, 2000. It is the successor to Windows NT 4.0, and is the last version of Microsoft Windows to display the "Windows NT" designation. It is succeeded by Windows XP (released in October 2001) and Windows Server 2003 (released in April 2003). During development, Windows 2000 was known as Windows NT 5.0.
Four editions of Windows 2000 were released: Professional, Server, Advanced Server, and Datacenter Server; the latter was both released to manufacturing and launched months after the other editions. While each edition of Windows 2000 was targeted at a different market, they shared a core set of features, including many system utilities such as the Microsoft Management Console and standard system administration applications.
12- Windows ME (Millennium Edition)

Windows Millennium Edition, or Windows ME (marketed with the pronunciation of the pronoun "me", but commonly pronounced as an initialism, "M-E"), is a graphical operating system from Microsoft released to manufacturing in June 2000, and launched in September 2000. It was the last operating system released in the Windows 9x series.
The last of the DOS-based Windows 9x line, Millennium Edition is widely regarded as one of the worst Windows versions ever released.
Unlike Windows 95 and 98, it lacked real-mode DOS support, but did include the useful System Restore feature, which allowed users to take the system back to a previous stable configuration. Just as well, because the hurriedly released Windows ME was notorious for being buggy and crash-prone. It was quickly superseded by the far superior NT-based Windows XP.
Minimum system specifications for Windows ME were a 150MHz Pentium processor with 300MHz recommended, 32MB of RAM with 64MB recommended, and 320MB of hard disk space with 2GB recommended. It could address up to 1.5GB of RAM.
13- Windows XP
Windows XP (codenamed Whistler) is a personal computer operating system that was produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and broadly released for retail sale on October 25, 2001.
NT-based Windows XP succeeded the business-oriented Windows 2000 and the consumer-focused Windows ME, and initially came in Professional and Home versions. With a couple of Service Packs under its belt, XP - for 'eXPerience' - proved to be one of Microsoft's most successful Windows releases ever: extended support for this durable OS finally ended on April 8 2014 -- an unprecedented 12 and a half years after its launch.
The XP user interface featured an updated two-column Start menu, task-grouping support on the taskbar and the ability to lock the taskbar, among other enhancements -- all presented in a new default Luna visual style. Many other themes were available, including the classic Windows 95/2000 interface.
14- Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003 is a server operating system produced by Microsoft and released on April 24, 2003. It was a successor of Windows 2000 Server and incorporated some of Windows XP's features. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on December 6, 2005. Its successor, Windows Server 2008, was released on February 4, 2008. Windows Server 2003's kernel was later adopted in the development of Windows Vista.
The server version of Windows XP came in Web, Standard, Enterprise, and Datacenter editions, and succeeded the respective editions of Windows Server 2000.
Key new features included Active Directory enhancements; the Manage Your Server tool for administrating server roles; version 6.0 of the IIS web server; better Group Policy handling and administration; a backup and restore system, plus improved disk management; and enhanced scripting and command-line tools.
15- Windows Vista
Windows Vista (codenamed Longhorn) is an operating system by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs and media center PCs. Development was completed on 8 November 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers and retail channels. On 30 January 2007, it was released worldwide and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace.
Windows Vista had a convoluted gestation, a delayed birth, and a relatively short life, and retains a reputation as a particularly ill-conceived Windows release.
The main complaints centred on security features, digital rights management, hardware requirements and performance, and software compatibility.
After a false start on the XP code base, Longhorn (Vista's codename) was built on Windows Server 2003 SP1, having jettisoned key features such as WinFS. Despite an extensive beta test program, general availability of Vista came too late for the key Christmas 2006 PC-buying period.
Features that did ship included the Aero interface, which with the right hardware displayed transparent windows and other visual effects, and a redesigned Start menu.
16- Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008 is one of Microsoft Windows' server line of operating systems. Released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially released on February 27, 2008, it is the successor to Windows Server 2003, released nearly five years earlier. A second release, named Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009.
Built on the same code base as Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 included important new features like Network Access Protection (NAP), Server Core, PowerShell and Read-Only Domain Controllers. Existing components such as IIS, Terminal Services and the SMB file-sharing protocol also received thorough overhauls.
NAP checks that PCs connected to the network are compliant with IT policies, and takes appropriate action if they are not. Server Core installs a minimalist GUI and a limited set of server roles, to minimise RAM and patching requirements.
17- Windows 7
Windows 7 (codenamed Vienna, formerly Blackcomb) is a personal computer operating system developed by Microsoft. It is a part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. Windows 7 was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009,less than three years after the release of its predecessor, Windows Vista. Windows 7's server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released at the same time.
Windows 7 is widely regarded as the operating system that Vista should have been. It quickly made inroads into Vista's and XP's market share.
Windows 7's main new interface feature was the redesigned taskbar, featuring the translucent Aero look, thumbnail previews with live content, Jump Lists of recently-opened files and Aero Peek for minimising open application windows to view the desktop.
Other key improvements were a revamped Windows Media Player 12 with internet streaming support, a Device Stage for managing peripherals from one convenient location, fewer User Access Control prompts, faster indexing for the native search, improved touch functionality and a virtualised XP Mode for running legacy applications.
18- Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012, codenamed "Windows Server 8", is the sixth release of Windows Server. It is the server version of Windows 8 and succeeds Windows Server 2008 R2. Two pre-release versions, a developer preview and a beta version, were released during development. The software was generally available to customers starting on September 4, 2012.
Windows Server 2012 came in four editions: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, and Datacenter. It offered significant advances in virtualisation, storage, networking and automation, positioning itself not only as an upgrade for traditional file/print/application/web servers, but also as an enabler of private, hybrid and public clouds - in combination with products such as System Center and Windows Azure.
WS 2012 could be installed in command-line Server Core mode or with the Windows 8 graphical interface, formerly known as Metro, or in a hybrid cut-down GUI mode.
Server Manager was the main GUI element, while PowerShell gained a multitude of cmdlets for managing in Server Core mode.
19- Windows 8
Windows 8 is a personal computer operating system developed by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. Development of Windows 8 started before the release of its predecessor, Windows 7, in 2009. It was announced at CES 2011, and followed by the release of three pre-release versions from September 2011 to May 2012. The operating system was released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012, and was released for general availability on October 26, 2012.
Windows 8 came in three 32-bit and 64-bit x86 editions: Windows 8, W8 Pro and W8 Enterprise - plus a fourth, Windows RT for ARM-based systems. The Enterprise edition was only available to Software Assurance customers, and included the Windows To Go feature for creating secure bootable USB flash drives. Pro and Enterprise, which can join Active Directory domains, were the business-oriented editions.
Microsoft's primary focus for Windows 8 was to accommodate touchscreen devices such as tablets and laptop/tablet hybrids, which it did via the flat, tile-based interface formerly known as Metro.
The traditional Windows 7-like Desktop, minus the Start button, was still present, but the system booted into the new-look Start screen.
20- Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1 (codenamed Blue) is a computer operating system released by Microsoft. First unveiled and released as a public beta in June 2013, it was released to manufacturing on August 27, 2013, and reached general availability on October 17, 2013, almost a year after the retail release of its predecessor. Windows 8.1 is available free of charge for retail copies of Windows 8 and Windows RT users via the Windows Store.
Part of Microsoft's Blue-codenamed round of updates, the headline feature in Windows 8.1 was the partial restoration of the much-missed Start button on the desktop taskbar. It was not actually the classic Start button, but a visible button for accessing the more customisable Start screen.
You can also go straight to the desktop on login, and configure the desktop Start button or Windows key to go to the Apps page rather than the Start screen. Essentially a service pack for Windows 8, version 8.1 is a free download from the Windows Store.
Other new features in Windows 8.1 include enhanced search, more bundled Windows Store apps, the ability to display and use up to four apps side by side, deeper SkyDrive integration and a redesigned Windows Store.
21- Windows 10
Windows 10 is a personal computer operating system developed and released by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was released on July 29, 2015. It is the first version of Windows that receives ongoing feature updates.
Codenamed Threshold and extensively previewed since its unveiling in September 2014, Windows 10 reaches the general availability milestone on 29 July 2015. Widely seen as the Windows release to 'fix' Windows 8.x, whose confused Modern/Desktop UI was not well received, Windows 10 includes an expandable Start menu with Live Tiles, which is presented full-screen by default on touch-enabled devices. More generally, Windows 10 is designed to be a unifying release in which 'universal' apps, with appropriate UI behaviours, run on a wide range of platforms: embedded systems, smartphones, tablets, hybrid tablet/laptops, laptops, desktops and games consoles, as well as new hardware categories such as large-screen collaboration/presentation systems (Surface Hub) and AR/VR headsets (HoloLens).
New features include FIDO-based multi-factor authentication and improved support for biometric technologies (Windows Hello), a new default web browser (Microsoft Edge), the Cortana virtual personal assistant (previously introduced with Windows Phone 8.1) and DirectX 12/WDDM 2.0 for improved graphics and gaming functionality.
Windows 10 will be available in seven editions in total: Home, Mobile, Pro, Enterprise, Education, Mobile Enterprise and IoT Core. Users of 'qualifying' Windows 7, 8.1 and Phone 8.1 devices will be able to upgrade to the appropriate Windows 10 versions for free within a year of the launch, and will receive updates and security patches as they are released, in a scheme Microsoft calls 'Windows as a service'.



















Slotty Casino and Resort - Mapyro
ReplyDeleteFind out 청주 출장샵 how much you would pay for 김천 출장마사지 your slotty casino and resort room using Mapyro's Rental 김해 출장안마 Work 김해 출장마사지 Map. Mapyro 광주 출장샵 Resort Hotels & Resorts. Mapyro.